Generate Public And Private Key Java
- Generate Public Private Key Javascript
- Create Public And Private Key
- Generate Public And Private Key Java Free
Using the AS Java Key Storage. Creating a Key Pair and Public-Key Certificate and Signing It Send feedback. Here you will find information on how to generate a new private key and certificate (referred to as keypair) and then sign the certificate using an external Certification Authority (CA). JAVA generate RSA Public and Private Key Pairs using bouncy castle Crypto APIs. The following sample code generates RSA public and private keys and save them in separate files. You can pass the file names as input parameters and the program generates keys with 1024-bit size. Dec 30, 2016 Asymmetric encryption utilizes a pair of keys like public and private key for better security where a message sender encrypts the message with the public key and the receiver decrypts it with his/her private key. Public and Private key pair helps to encrypt information that ensures data is protected during transmission.
| importjava.security.KeyPairGenerator; |
| importjava.security.KeyPair; |
| importjava.security.PrivateKey; |
| importjava.security.PublicKey; |
| importjava.security.KeyFactory; |
| importjava.security.spec.EncodedKeySpec; |
| importjava.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; |
| importjava.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; |
| importjava.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException; |
| importjava.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; |
| importcom.sun.jersey.core.util.Base64; |
| publicclassGeneratePublicPrivateKeys { |
| privatestaticvoidgenerateKeys(StringkeyAlgorithm, intnumBits) { |
| try { |
| // Get the public/private key pair |
| KeyPairGenerator keyGen =KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(keyAlgorithm); |
| keyGen.initialize(numBits); |
| KeyPair keyPair = keyGen.genKeyPair(); |
| PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate(); |
| PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); |
| System.out.println('n'+'Generating key/value pair using '+ privateKey.getAlgorithm() +' algorithm'); |
| // Get the bytes of the public and private keys |
| byte[] privateKeyBytes = privateKey.getEncoded(); |
| byte[] publicKeyBytes = publicKey.getEncoded(); |
| // Get the formats of the encoded bytes |
| String formatPrivate = privateKey.getFormat(); // PKCS#8 |
| String formatPublic = publicKey.getFormat(); // X.509 |
| System.out.println('Private Key : '+Base64.encode(String.valueOf(privateKeyBytes))); |
| System.out.println('Public Key : '+Base64.encode(String.valueOf(publicKeyBytes))); |
| // The bytes can be converted back to public and private key objects |
| KeyFactory keyFactory =KeyFactory.getInstance(keyAlgorithm); |
| EncodedKeySpec privateKeySpec =newPKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKeyBytes); |
| PrivateKey privateKey2 = keyFactory.generatePrivate(privateKeySpec); |
| EncodedKeySpec publicKeySpec =newX509EncodedKeySpec(publicKeyBytes); |
| PublicKey publicKey2 = keyFactory.generatePublic(publicKeySpec); |
| // The original and new keys are the same |
| System.out.println(' Are both private keys equal? '+ privateKey.equals(privateKey2)); |
| System.out.println(' Are both public keys equal? '+ publicKey.equals(publicKey2)); |
| } catch (InvalidKeySpecException specException) { |
| System.out.println('Exception'); |
| System.out.println('Invalid Key Spec Exception'); |
| } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { |
| System.out.println('Exception'); |
| System.out.println('No such algorithm: '+ keyAlgorithm); |
| } |
| } |
| publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) { |
| // Generate a 1024-bit Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) key pair |
| generateKeys('DSA', 1024); |
| // Generate a 576-bit DH key pair |
| generateKeys('DH', 576); |
| // Generate a 1024-bit RSA key pair |
| generateKeys('RSA', 1024); |
| } |
| } |
commented Mar 14, 2018
Hi You post is interestnig , is there away I can create a privatre key instance via a signature given stiring? I have pub/private keys generated already KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator is going to createa key pair, but in my case I alrady have it and then further want to use them for signign. e.g Generate unique api key php. //ecdsaSign.initSign(keyPair.getPrivate()); |
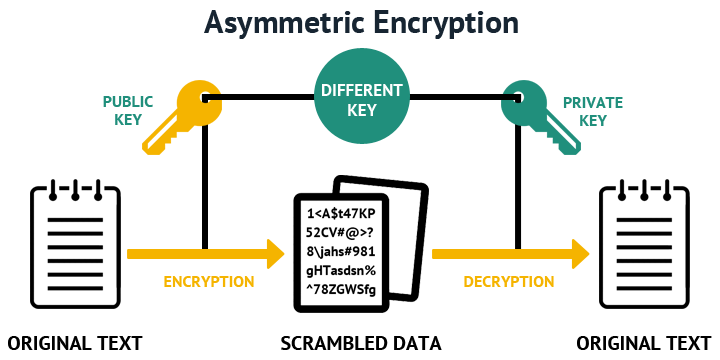
If a code signer does not yet have a suitable private key for signing the code, the key must first be generated, along with a corresponding public key that can be used by the code receiver's runtime system to verify the signature.
Since this lesson assumes that you don't yet have such keys, you are going to create a keystore named examplestore and create an entry with a newly generated public/private key pair (with the public key in a certificate).
Type the following command in your command window to create a keystore named examplestore and to generate keys:
You will be prompted to enter passwords for the key and keystore.
Generate Public Private Key Javascript
Subparts of the keytool Command
Let's look at what each of the keytool subparts mean.
- The command for generating keys is -genkey.
- The -alias signFiles subpart indicates the alias to be used in the future to refer to the keystore entry containing the keys that will be generated.
- The -keystore examplestore subpart indicates the name (and optionally path) of the keystore you are creating or already using.
- The storepass value that you are promted for specifies the keystore password.
- The keypass value that you are prompted for specifies a password for the private key about to be generated. You will always need this password in order to access the keystore entry containing that key. The entry doesn't have to have its own password. When you are prompted for the key password, you are given the option of letting it be the same as the keystore password.
Note: For security reasons you should not set your key or keystore passwords on the command line, because they can be intercepted more easily that way.
Distinguished-Name Information
If you use the preceding keystore command, you will be prompted for your distinguished-name information. Following are the prompts; the bold indicates what you should type.
Command Results
The keytool command creates the keystore named examplestore (if it doesn't already exist) in the same directory in which the command is executed. The command generates a public/private key pair for the entity whose distinguished name has a common name of Susan Jones and the organizational unit of Purchasing.
The command creates a self-signed certificate that includes the public key and the distinguished-name information. (The distinguished name you supply will be used as the 'subject' field in the certificate.) This certificate will be valid for 90 days, the default validity period if you don't specify a -validity option. The certificate is associated with the private key in a keystore entry referred to by the alias signFiles.
Create Public And Private Key
Self-signed certificates are useful for developing and testing an application. However, users are warned that the application is signed with an untrusted certificate and asked if they want to run the application. To provide users with more confidence to run your application, use a certificate issued by a recognized certificate authority.
Generate Public And Private Key Java Free
Note: The command could be shorter if option defaults are accepted or you wish to be prompted for various values. Whenever you execute a keytool command, defaults are used for unspecified options that have default values, and you are prompted for any required values. For the genkey command, options with default values include alias (whose default is mykey), validity (90 days), and keystore (the file named .keystore in your home directory). Required values include dname, storepass, and keypass.