Bash Script Generate Ssh Key
This is quite a common task for Linux system administrators, when it is needed to execute some command or a local Bash script from a one Linux workstation or a server on another remote Linux machine over SSH.
- Bash Script Generate Ssh Key Windows
- Create Ssh Key Git Bash
- Bash Script Generate Ssh Key
- Generate Ssh Key In Bash
In this article you will find the examples of how to execute a remote command, multiple commands or a Bash script over SSH between remote Linux hosts and get back the output (result).
This information will be especially useful for ones, who want to create a Bash script that will be hosted locally on a one Linux machine but would be executed remotely on the other hosts over SSH.
Cool Tip: Connect to a remote SSH server without typing a password! Configure a passwordless authentication! Only 3 easy steps! Read more →
SSH into your VM with the ssh cmd. Ssh username@ipaddress Upon establishing the SSH connection, you should see the Ubuntu welcome prompt. Exit your ssh session. Exit Delete your resource group and any resources within it. Az group delete -n MyRG Next steps. Learn about persisting files for Bash in Cloud Shell Learn about Azure CLI. Create an SSH key. Follow these steps if you don't already have an SSH key for an account. If you do have an SSH key and you want to generate another key, you'll have to use the terminal because you can't use Sourcetree to create a second key. Creating an SSH key looks something like this: From the Sourcetree menu, select Preferences. $ cd /.ssh $ ls authorizedkeys2 iddsa knownhosts config iddsa.pub You’re looking for a pair of files named something like iddsa or idrsa and a matching file with a.pub extension. The.pub file is your public key, and the other file is the corresponding private key. If you don’t have. The first step in the installation process is to create the key pair on the client machine, which would, more often than not, be your own system. Users need to use the following command: ssh-keygen -o -b 4096 -t rsa. The above command kicks off the SSH Key installation process for users. Apr 14, 2020 I configured authentication by ssh key and it works but when I restart the servers, they lose the authentication. I would like to know if I can create an ssh script which allows to launch the authentication at startup of the machines without entering the passphrase each time. Generating a new SSH key. Open Terminal Terminal Git Bash. Paste the text below, substituting in your GitHub email address. $ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C 'youremail@example.com' This creates a new ssh key, using the provided email as a label. Generating public/private rsa key pair.
SSH: Execute Remote Command
Execute a remote command on a host over SSH:
Examples
Get the uptime of the remote server:
Reboot the remote server:
SSH: Run Multiple Remote Commands
In the most cases it is not enough to send only one remote command over SSH.Much more often it is required to send multiple commands on a remote server, for example, to collect some data for inventory and get back the result.
There are a lot of different ways of how it can be done, but i will show the most popular of them.
Run multiple command on a remote host over SSH:
– or –
– or –
Cool Tip: SSH login is too slow? This can be fixed easily! Get rid of delay during authentication! Read more →
Examples
Get the uptime and the disk usage:
Get the memory usage and the load average:
Show the kernel version, number of CPUs and the total RAM:
SSH: Run Bash Script on Remote Server
The equally common situation, when there is some Bash script on a Linux machine and it needs to connect from it over SSH to another Linux machine and run this script there.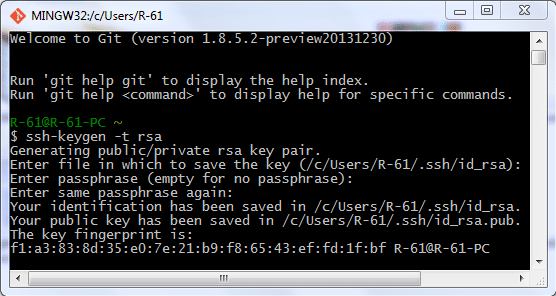
The idea is to connect to a remote Linux server over SSH, let the script do the required operations and return back to local, without need not to upload this script to a remote server.
Certainly this can be done and moreover quite easily.
Cool Tip: Want to ROCK? Start a GUI (graphical) application on a remote Linux workstation over SSH! Read more →
Example
Execute the local script.sh on the remote server:
You need to use the ssh-copy-id script that uses ssh to log into a remote machine using a login password. The syntax is as follows:
ssh-copy-id user@server.example.com[donotprint][/donotprint]
OR
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub user@server1.cyberciti.biz
OR
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_dsa.pub user@server1.cyberciti.biz
OR use specific port on remote host such as tcp port # 4242:
ssh-copy-id -i /path/key/file.pub 'user@server.example.com -p 4242'
Bash Script Generate Ssh Key Windows
Install ssh-copy-id on a OS X Unix systems
Type the following command:
Sample outputs:
Step # 1: Create the Keys
Type the following ssh-keygen command to generates, manages and converts authentication keys for your workstation / laptop:ssh-keygen
Make sure you protect keys with the passphrase.
Create Ssh Key Git Bash
Step # 2: Install the public key
Install key in a remote server called www-03.nixcraft.in, enter:ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub username@www-03.nixcraft.in
Bash Script Generate Ssh Key
Note: If ssh-copy-id command not found on your system, try the following commands to append/install the public key on remote host:
ssh username@www-03.nixcraft.in 'umask 077; mkdir .ssh'
cat $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub ssh username@www-03.nixcraft.in 'cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys'
Step #3: Use keychain for password less login
OpenSSH offers RSA and DSA authentication to remote systems without supplying a password. keychain is a special bash script designed to make key-based authentication incredibly convenient and flexible (see how to install keychain script on unix). Add following lines to your ~/.bash_profile or shell login file:
Save and close the file.
References:
- Man pages – ssh-copy-id(1)
Generate Ssh Key In Bash
ADVERTISEMENTS